Tailbone Pain
Have you ever experienced extreme pain on your tailbone when getting up from sitting? Have you felt tailbone pain during sexual intercourse? Have you experienced muscle spasm around the tailbone after having a bowel movement? If you have experienced any of these symptoms then you might have a condition called ‘Coccydynia’.
Today, we are going to talk about etiology and management of Coccydynia.
Anatomy of the Coccyx
The Coccyx is a small bone located below the sacrum and at the end of the spine. The coccyx is usually fused with 3~5 bones and surrounded by various ligaments and discs. The front of the coccyx is the attachment site for many ligaments and muscles.
One muscle group that attaches to your coccyx is your pelvic floor. All of the deep layers of pelvic floor muscles and some of the superficial layer of pelvic floor muscles have the coccyx as their attachment sites. When you have a problem with the coccyx, it is mostly likely to affect the pelvic floor muscles. On the other hand, when you have a problem on the pelvic floor muscles, it can also cause some issues on the coccyx. Additionally, there is a nerve passing along the side of the coccyx. This is called sacrococcygeal nerve. It innervates area of skin that surrounds the sacrum and coccyx.
Causes of Coccydynia
Based on the statistics, women are 5x more likely get a coccydynia than men. Adolescents and adults are more likely to present with coccydynia than children. The main causes for Coccydynia are…
- Pregnancy and childbirth: During pregnancy, the head of fetus generally sits on the coccyx. As the fetus is growing bigger, more pressure is exerted on the coccyx and it can cause strain on the pelvic floor muscles. It also is possible to fracture the coccyx during childbirth.
- Sitting for extended periods: Many people experience tailbone pain after sitting on a bicycle or hard surfaces for extended time. It’s because some sitting postures can exert more physical stress on the coccyx. Especially, slouched sitting distributes excessive pressure on the coccyx and can lead to coccydynia.
- Direct trauma: Falling backwards on a slippery floor during shower, falling from horse riding, or any other direct trauma on the coccyx can cause coccydynia.
- Over functioning of pelvic floor muscles: As it is stated in the previous section, the pelvic floor muscles are attached on the both side of the coccyx. If the pelvic floor muscles are over functioning, especially if one side of the pelvic floor muscles has more severe over-functioning, it could pull the coccyx to one side with uneven tension and can causes coccydynia.
How is it managed?
Recognizing proper body mechanics
Proper sitting posture with neutral spine should evenly distribute pressure from the weight of your body between your sit bones (ischial tuberosities) and coccyx. However, in slouched sitting posture, coccyx will withstand greater pressure than the sit bones, and the pelvic floor muscles around the coccyx take on excessive mechanical stress.
Same concept will be applied if you have a habit to shift your body weight to one side, or sleeping on one side, or sitting slanted to one side. Uneven pressure exerted on the spine can also be a source of stress to the coccyx as it is located on the bottom of it.
Consider a Wedge
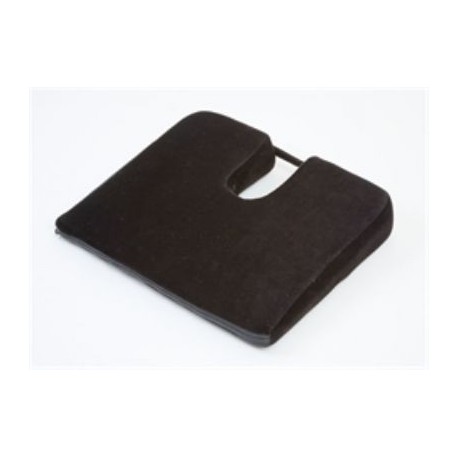 If you have to sit for long time for your work, I would recommend using the cushion that is specifically designed the tailbone pain with a cutout in back for the coccyx. This cushion reduces direct pressure on the coccyx and helps blood circulation.
If you have to sit for long time for your work, I would recommend using the cushion that is specifically designed the tailbone pain with a cutout in back for the coccyx. This cushion reduces direct pressure on the coccyx and helps blood circulation.
Ice or heat pack
Ice can reduce swelling from coccydynia and help eases pain. If you prefer to use hot rather than cold, then you can use a heat pack to reduce the pain. But it is recommended to avoid using the heat pack if you experienced recent trauma to the tailbone area, at least for the first 2~3 weeks.
Pelvic floor relaxation technique
Some patients with coccydynia have over-functioning of the pelvic floor muscles. Especially, if you have pain on the pelvic floor muscles during sexual intercourse or experience pain from sudden muscle spasm around the coccyx, then there is high likelihood that you have over functioning of the pelvic floor muscles.
When increased tension from the over functioning of the pelvic floor muscles continues, it could worsen the pain. So, it is important to try release the tightness and tension of pelvic floor muscles.
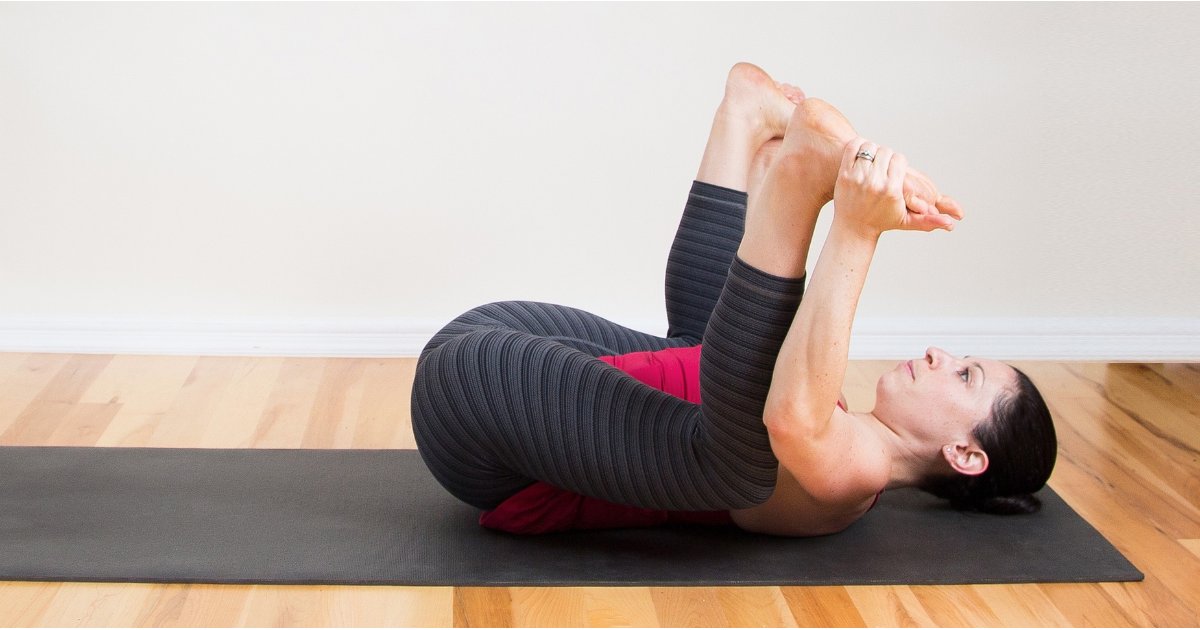
One easy stretch that you can do at home is called ‘happy baby stretch’. This stretch helps stretch your gluteus muscle that surrounds the sacrum and the coccyx, and it releases the tension on the pelvic floor muscles.
 Another easy way to loosen up the muscle is using a tennis ball. Place the tennis ball between the hip muscle and wall, lean your body towards the wall, move around your hip up and down or make circular motion, this will loosen up the muscle with the pressure of the tennis ball. If you find more tighten muscles, try to apply sustain pressure with the tennis ball to get that released.
Another easy way to loosen up the muscle is using a tennis ball. Place the tennis ball between the hip muscle and wall, lean your body towards the wall, move around your hip up and down or make circular motion, this will loosen up the muscle with the pressure of the tennis ball. If you find more tighten muscles, try to apply sustain pressure with the tennis ball to get that released.
Women’s Health Physical Therapy
Alignment of lumbar spine/pelvis
Your lumbar spine is located right above the sacrum and the coccyx. If your lumbar spine is out of alignment, the ligament that connects the lumbar spine and the sacrum/coccyx can get excessive tension, and can change the way that coccyx sits at the bottom of your spine. If there is a problem in alignment of the sacrum and the coccyx, it could cause the dysfunctions of pelvic floor muscles.
During the evaluation sessions with your women’s/men’s health physical therapist, biomechanical assessments of your lumbar spine and pelvis will be made. Based on the information obtained from the assessments, any positive findings (for example, muscle imbalance, too much/or lack of movements in your spine etc.) can be addressed with various therapeutic treatment approaches.
Pelvic floor rehabilitation
As mentioned before, the pelvic floor muscles surround the coccyx. Thus, if there are dysfunctions in your pelvic floor muscle, it is not going to be easy to manage the coccydynia. Your women’s/men’s health physical therapist will be able to find any dysfunctions in your pelvic floor muscles (whether that is weakness, over-functioning, instability or incoordination) and help you address those issues, https://clubgreenwood.com/soma-carisoprodol/.
The pelvic floor muscles support the rectum, womb/vagina, bladder/urethra. For this reason, your bladder and bowel functions should be functioning fairly well to keep your pelvic floor healthy. Various pelvic floor dysfunctions can be caused by those issues and will delay the recovery process. For example, if you have severe constipation, it can strain your pelvic floor muscles with excessive downward pressure as it supports your rectum. Thus, if any of your bladder or bowel issues has not be managed well, it is going to be very challenging to get rid of tailbone pain completely or avoid recurrence of Coccydynia.
If you have any pelvic floor muscles issues such as urinary/fecal incontinence and constipation, I highly recommend you to see a women’s/men’s health physical therapist. Your physical therapist will be able to assess any dysfunctions in your pelvic floor muscle and provide you appropriate treatment to help you return to the lifestyle you deserve.
References:
- Johnson, A., & Rochester, A. P. (2006). coccydynia. Journal of Women’s Health Physical Therapy, 30(2), 40.
- Howard, P. D., Dolan, A. N., Falco, A. N., Holland, B. M., Wilkinson, C. F., & Zink, A. M. (2013). A comparison of conservative interventions and their effectiveness for coccydynia: a systematic review. Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy, 21(4), 213-219.
- Bradley, M. H., Rawlins, A., & Brinker, C. A. (2017). Physical therapy treatment of pelvic pain. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics, 28(3), 589-601.
- Polsdorfer, R. (1992). Three Case Studies: Coccydynia and the Orthopaedic Rectal Examination. Journal of Orthopaedic Medicine, 14(1), 13-17.
By Hyunhye Lee, PT, DPT, CLT
ALSO SEE : What is Overactive Bladder?